Summary
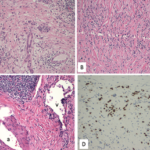
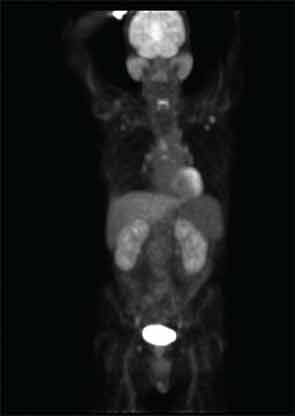
Our patient had a multiorgan system disease of at least two years’ duration characterized by tubulointerstitial nephritis, salivary gland enlargement, jaundice, diffuse lymphadenopathy, and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate. In addition, it is likely that his pancreatitis, which led to glucose intolerance, was in fact IgG4-related (type 1) autoimmune pancreatitis. He was misdiagnosed with a number of other conditions before the correct diagnosis of IgG4-RD was recognized.
IgG4-RD is a newly recognized entity, but in fact it is an old one. The disease can involve multiple organ systems, frequently in a metachronous fashion (i.e., first one organ, then another, and then another). The disease tends to cause mass-forming lesions that can mimic cancer, infections, and rheumatic conditions such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s) and SS. This disease is responsible for substantial percentages of cases—and sometimes all cases—of a variety of clinical entities previously referred to by other names (e.g., retroperitoneal fibrosis, Riedel’s thyroiditis, Mikulicz disease, Küttner’s tumor, and others).
Most patients respond well to glucocorticoids, but many are unable to discontinue these medications without disease recurrence. B-cell depletion is a promising treatment strategy now under investigation.
Follow-up
Because of his glucose intolerance and the extensive nature of his disease, we treated our patient with rituximab 1 gram intravenously given on two separate occasions. Within one month of his first dose, his parotid gland swelling had resolved, and his serum IgG4 concentration had declined by more than 600 mg/dL. He is currently enrolled in an ongoing clinical trial.
Dr. Atac is a visiting researcher at the Massachusetts General Hospital. Dr. Stone is a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of clinical rheumatology at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
References
- Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:539-551.
- Kamisawa T, Egawa N, Nakajima H. Autoimmune pancreatitis is a systemic autoimmune disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:2811-2812.
- Yoshida K, Toki F, Takeuchi T, et al. Chronic pancreatitis caused by an autoimmune abnormality. Proposal of the concept of autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1995;40:1561-1568.
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:732-738.
- Khosroshahi A, Stone JH. A clinical overview of IgG4-related systemic disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23:57-66.
- Pace C, Ward S. A rare case of IgG4-related sclerosing disease of the maxillary sinus associated with bone destruction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68:2591-2593.
- Kamisawa T, Anjiki H, Egawa N, Kubota N. Allergic manifestations in autoimmune pancreatitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;21:1136-1139.
- Zen Y, Nakanuma Y. IgG4-related disease: A cross-sectional study of 114 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34:1812-1819.
- Deshpande V, Gupta R, Sainani N, et al. Subclassification of autoimmune pancreatitis: A histologic classification with clinical significance. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35:26-35.
- Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012; 25:1181-1192.
- Khosroshahi A, Cheryk LA, Carruthers MN, et al. Prozone phenomenon leads to low IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-related disease (Abstract 2527). Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(10 Suppl):S1067.
- Chang WI, Kim BJ, Lee JK, et al. The clinical and radiological characteristics of mass-forming autoimmune pancreatitis: Comparion with chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Pancreas. 2009;38:401-408.
- Zen Y, Inoue D, Kitao A et al. IgG4-related lung and pleural disease: A clinicopathologic study of 21 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33:1886-1893.
- Cheuk W, Yuen HK, Chu SY, et al. Lymphadenopathy of IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32:671-681.
- Kamisawa T, Shimosegawa T, Okazaki K, et al. Standard steroid treatment for autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2009;58:1504-1507.
- Ghazale A, Chari ST, Zhang L, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis: Clinical profile and response to therapy. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:706-715.
- Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MN, Deshpande V, et al. Rituximab for the treatment of IgG4-related disease: Lessons from 10 consecutive patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2012;91:57-66.
- Khosroshahi A, Bloch DB, Deshpande V, Stone JH. Rituximab therapy leads to rapid decline of serum IgG4 levels and prompt clinical improvement in IgG4-related systemic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:1755-1756.
- Stone JH, Khosroshahi A, Deshpande V, et al. Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:3061-3067.