When to obtain imaging, particularly when results would likely lead to treatment changes: Because symptoms and the physical exam can be nonspecific, Dr. Ward says it is occasionally difficult to know if new or ongoing pain and stiffness in the spine or pelvis represents ongoing disease activity in patients who are already taking a biologic. In these cases, MRI was conditionally recommended because finding evidence of inflammation on imaging in these cases may support a change in medication or in dose.
Alternatively, the recommendation is against obtaining MRIs to look for occult inflammation in patients who are clinically doing well. The guideline also includes a conditional recommendation against routine X-rays of the spine or pelvis on a regularly scheduled basis to monitor progression, because these will not change treatment in most cases. “This does not apply to situations when new symptoms develop that warrant investigation,” Dr. Ward says.
Implementation Support
Figure 1 in the guideline provides a comprehensive graphic overview of key treatment actions for patients with active AS and stable AS. The figure is designed to help practitioners determine treatment approaches according to first-, second- and third-line therapies and delineated by recommendation strength.
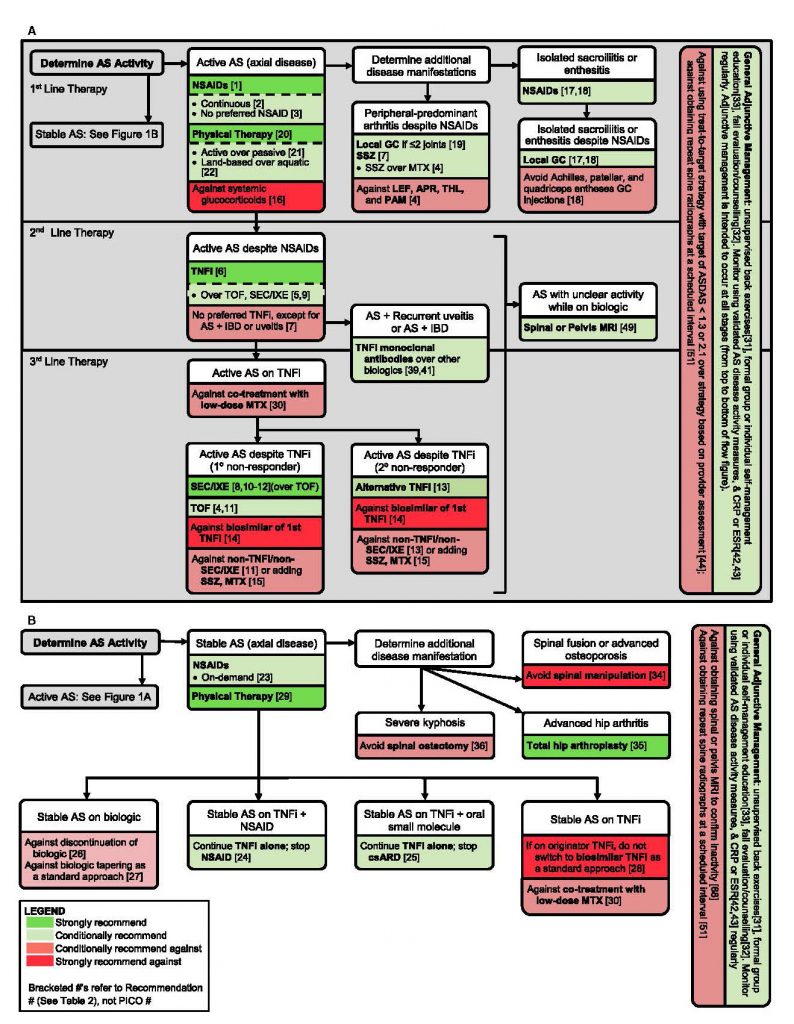
Figure 1. A comprehensive graphic overview of key treatment actions for patients with active AS and stable AS.
“We hope the figure presents an easy-to-follow capsule summary of the main recommendations,” Dr. Ward says. The ACR is also planning to develop a pocket card, as well as add the guideline to its mobile app.
“The ultimate goal in releasing this guideline update is to speed patient receipt of appropriate medications, while avoiding unnecessary imaging procedures and, ultimately, improving symptoms and health status for patients with axial SpA,” says Dr. Ward.
Carina Stanton is a freelance science journalist based in Denver.
References
- Ward MM, Deodhar A, Gensler LS, et al. 2019 Update of the American College of Rheumatology/Spondylitis Association of America/Spondylitis Association of America/Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network Recommendations for the Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis and Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2019 Aug 21. [Epub ahead of print]
- About Spondylitis. Spondylitis Association of America.
- Baeton D, Sieper J, Braun J, et al. Secukinumab, an interleukin-17A inhibitor, in ankylosing spondylitis. N Engl J Med. 2015 Dec 24;373(26):2534–2548.
- van der Heijde D, Cheng-Chung Wei J, Dougados M, et al. Ixekizumab, an interleukin-17A antagonist in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis or radiographic axial spondyloarthritis in patients previously untreated with biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (COAST-V): 16 week results of a phase 3 randomised, double-blind, active-controlled and placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2018 Dec 8;392(10163):2441–2451.