Approximately 80% of hypertrophic osteoarthropathy cases are due to a primary or secondary pulmonary malignancy.
The patient’s laboratory workup demonstrated an angiotensin-1-converting enzyme level of 33 U/L (RR: 6–97). The ANA was positive, with both a nucleolar pattern (with a titer of 1:160) and a speckled pattern (with a titer of 1:40). The cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) antibody test was less than 16 units (RR: <16).
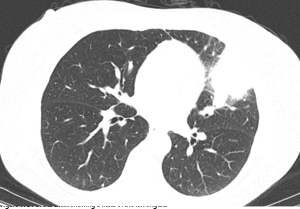
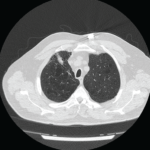
Figure 1: CT of the chest showing a mass in the left lingula.
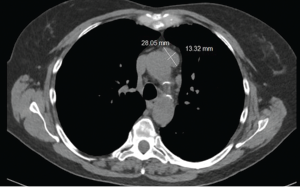
Figure 2: CT of the chest showing a mass in anterior mediastinum.
Serum protein electrophoresis revealed an alpha 1 globulin level of 0.4 g/dL (RR: 0.2–0.3), alpha 2 globulin level of 0.8 g/dL (RR: 0.5–0.9), gamma globulin level of 0.8 g/dL (RR: 0.8–1.7), beta 1 globulin level of 0.4 g/dL (RR: 0.4–0.6), and beta 2 globulin level of 0.3 g/dL (RR: 0.2–0.5).
The sedimentation rate was 29 (RR: ≤30). Her C-reactive protein level was elevated at 15.8 mg/L (RR: <8).
The CT scan of the chest was notable for several findings. An irregular, ill-defined, large, 6×5.6 cm mass was identified in the lingula, with associated adenopathy in the left hilum and anterior mediastinum. Several sub-centimeter noncalcified nodular densities were found in the right lower lobe, but because they were present on prior imaging studies, they were considered to have a benign etiology.
Imaging of the extremities was notable for periostosis involving the tibia and fibula, bilaterally. No effusions, erosions, chondrocalcinosis or destructive process were identified on the imaging studies of the extremities.
The patient was sent for a lung biopsy and positron emission tomography (PET) scan. The PET scan showed a metabolically active site in the left lung compatible with malignancy. Mediastinal and left hilar lymph node metastases were also identified on the PET scan.
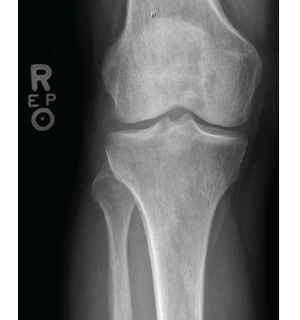
Figure 3: X-ray of the right knee showing periostosis of
the fibula and tibia.
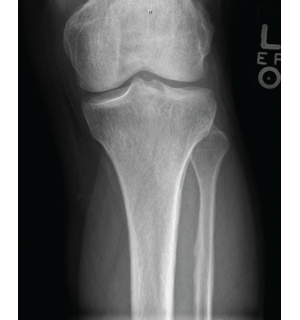
Figure 4: X-ray of the left knee showing periostosis of the fibula and tibia.
The lung biopsy demonstrated a non-small cell carcinoma. The patient was diagnosed as having hypertrophic osteoarthropathy (HOA) secondary to a primary lung malignancy. She was referred to an oncologist for further management.
The oncologist ordered magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the patient’s brain, which did not demonstrate metastatic disease. Weekly carboplatin and paclitaxel were initiated, with concurrent radiation.
At the patient’s last encounter with the rheumatology clinic, her arthralgias were not noticeably improving with nabumetone, so she was transitioned to celecoxib. Her arthralgias improved significantly with the medication change.