Conclusion
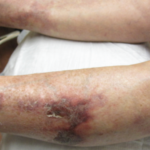
Rheumatologists can play an important role in the diagnosis of Sneddon syndrome. In patients presenting with livedo racemosa, Sneddon syndrome should be included in the differential diagnosis, especially due to the high impact of potential disease complications. Additionally, when obtaining biopsies of livedo racemosa to investigate for histopathological evidence of Sneddon syndrome, an important consideration is whether the biopsied area is large enough for an accurate diagnosis.
It is vital to keep in mind the differential diagnosis in patients presenting with generalized livedo racemosa without evidence of positive antiphospholipid syndrome, especially in the context of known ischemic events. The lack of recognition of this rare syndrome can mean the difference between preventive anticoagulation and potential catastrophic events.
 Emily Jean Katz, PA-C, is a physician assistant practicing rheumatology at the Center for Rheumatology, Saratoga Springs, N.Y.
Emily Jean Katz, PA-C, is a physician assistant practicing rheumatology at the Center for Rheumatology, Saratoga Springs, N.Y.
Kelsey Hennig, PharmD, BCPS, is a clinical assistant professor at Binghamton University, New York. She previously completed a PGY-1 pharmacy practice residency at St. Joseph’s Health, Syracuse, N.Y., and a PGY-2 ambulatory care pharmacy residency at Albany College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, New York.
Mitchell Miller, PharmD, is a clinical pharmacy specialist in population health for Bassett Healthcare Network. He completed two years of post-graduate residency training, spending one year at St. Peter’s Hospital, Albany, N.Y., and another at Albany College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences.

Jessica Farrell, PharmD, is a clinical pharmacist practicing at the Center for Rheumatology and an associate professor in the Department of Pharmacy Practice at Albany College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences. Dr. Farrell is also a member of the ACR Government Affairs Committee.
Takeaways
- A diagnosis of Sneddon syndrome is best made via a multidisciplinary approach.
- Biopsy areas must be large enough to appreciate signs of Sneddon syndrome.
References
- Cleaver J, Teo M, Renowden S, et al. Sneddon syndrome: A case report exploring the current challenges faced with diagnosis and management. Case Rep Neurol. 2019 Dec 16;11(3):357–368.
- Wu S, Xu Z, Liang H. Sneddon’s syndrome: A comprehensive review of the literature. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014 Dec 13;9:215.
- Tietjen GE, Al-Qasmi MM, Gunda P, et al. Sneddon’s syndrome: Another migraine-stroke association? Cephalalgia. 2006 Mar; 26(3):225–232.
- Francès C, Papo T, Wechsler Bet al. Sneddon syndrome with or without antiphospholipid antibodies. A comparative study in 46 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1999 Jul;78(4):209–219.
- Bolayir E, Yilmaz A, Kugu N, et al. Sneddon’s syndrome: Clinical and laboratory analysis of 10 cases. Acta Med Okayama. 2004 Apr; 58(2):59–65.
- Coumadin (warfarin) prescribing information. Bristol-Meyers Squibb Company. 2019 Dec.