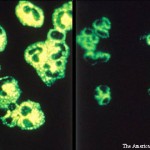
In mild cases of drug-induced autoinflammatory syndrome, cessation of the inciting agent is adequate to resolve further morbidity.
Historically, AAV and drug-induced lupus erythematosus have been considered mutually exclusive, but our case highlights an overlap, suggesting the possibility of a continuum between these conditions.
Additionally, hydralazine-associated AAV in the literature suggests a predominance of renal-limited vasculitis. Our case, however, describes pulmonary-renal syndrome.4,5
In mild cases of drug-induced autoimmune syndromes, cessation of the inciting agent is adequate to resolve further morbidity. However, our case suggests that drug cessation may not be enough to address the phenomenon of vasculitis and further immunosuppression may be warranted.
 Mohammad A. Ursani, MD, FACP, RhMSUS, is a private practice rheumatologist in The Woodlands, Texas, and serves as an adjunct faculty member for the University of Texas, Houston, Internal Medicine Residency Program. He also serves as a volunteer for the ACR and is a young physician ambassador for the Harris County Medical Society.
Mohammad A. Ursani, MD, FACP, RhMSUS, is a private practice rheumatologist in The Woodlands, Texas, and serves as an adjunct faculty member for the University of Texas, Houston, Internal Medicine Residency Program. He also serves as a volunteer for the ACR and is a young physician ambassador for the Harris County Medical Society.
 Ojas Naik, MD, is a private practice nephrologist at Kidney Specialists of North Houston with an interest in autoimmune manifestations of renal disease.
Ojas Naik, MD, is a private practice nephrologist at Kidney Specialists of North Houston with an interest in autoimmune manifestations of renal disease.
 Rohaan Khan is a health sciences student at Michael E. DeBakey High School for Health Professions and has an interest in pursuing a degree in medicine.
Rohaan Khan is a health sciences student at Michael E. DeBakey High School for Health Professions and has an interest in pursuing a degree in medicine.
 William F. Glass II, MD, PhD, is a professor and vice chair for graduate medical education, director of the pathology residency program and director of renal pathology services at the University of Texas, Houston.
William F. Glass II, MD, PhD, is a professor and vice chair for graduate medical education, director of the pathology residency program and director of renal pathology services at the University of Texas, Houston.
References
- Grau RG. Drug-induced vasculitis: New insights and a changing lineup of suspects. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015 Dec;17(12):71.
- Hogan JJ, Markowitz GS, Radhakrishnan J. Drug-induced glomerular disease: Immune-mediated injury. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Jul 7;10(7):1300–1310.
- Agarwal G, Sultan G, Werner SL, Hura C. Hydralazine induces myeloperoxidase and proteinase 3 anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody vasculitis and leads to pulmonary renal syndrome. Case Rep Nephrol. 2014;2014:868590.
- Yokogawa N, Vivino FB. Hydralazine-induced autoimmune disease: Comparison to idiopathic lupus and ANCA-positive vasculitis. Mod Rheumatol. 2009;19(3):338–347.
- Suneja M, Baiswar S, Vogelgesang SA. Hydralazine associated pauci-immune glomerulonephritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2014 Mar;20(2):99–102.