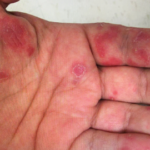
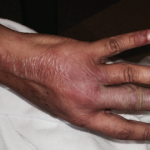
Another major problem with such drugs as lenalidomide and thalidomide is their exorbitant costs. Both thalidomide and lenalidomide have FDA-approved indications in cancer therapy. As such, their costs are extremely high in the U.S. In 2022, lenalidomide cost was ~$294,000 per year for the average person in the U.S. Because neither thalidomide nor lenalidomide has been FDA approved for either SLE or cutaneous lupus erythematosus, it would be difficult to convince a patient’s commercial medical insurer to cover the high costs of these drugs. However, if a lower income patient meets the company’s patient assistance program criteria, they could receive the drugs from the company without cost.
Other drugs that might be of benefit to refractory cutaneous lupus erythematosus include monthly high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin infusion (IVIG), belimumab, JAK/STAT intracellular signaling pathway inhibitors (e.g., tofacitinib, ruxolitinib, baricitinib), and interferon receptor inhibitors (e.g., anifrolumab). Tyk intracellular signaling inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies targeting plasmacytoid dendritic cells (e.g., anti-BDCA2, anti-ILT7) and cGAS-STING intracellular signaling inhibitors could be of potential clinical benefit for refractory cutaneous lupus erythematosus in the future.
While often underappreciated, comparative healthcare quality-of-life studies have shown that chronic skin disease is among the most debilitating of all medical illnesses. As space here is limited, the interested reader can find additional literature citations to relevant points of discussion in the text above in several recently published reviews on
this subject.6
Richard D. Sontheimer, MD, Professor (Clinical) of Dermatology and Board Certified in Internal Medicine, Dermatology, Dermatologic Immunology Department of Dermatology Spencer Fox Eccles School of Medicine, University of Utah.
References
- Sontheimer RD. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus: A decade’s perspective. Med Clin North Am. 1989 Sep;73(5):1073–1090.
- Belin DC, Bordwell BJ, Einarson ME, et al. Familial discoid lupus erythematosus associated with heterozygote C2 deficiency. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Aug;23(8):898–903.
- Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Amoura Z, Hulot JS, Hammoud HA, et al. Low blood concentration of hydroxychloroquine is a marker for and predictor of disease exacerbations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Oct;54(10):3284–3290.
- Sotgia S, Zinellu A, Mundula N, et al. A capillary electrophoresis-based method for the measurement of hydroxychloroquine and its active metabolite desethyl hydroxychloroquine in whole blood in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Molecules. 2022 Jun 17;27(12):3901.
- Cortés-Hernández J, Torres-Salido M, Castro-Marrero J, et al. Thalidomide in the treatment of refractory cutaneous lupus erythematosus: prognostic factors of clinical outcome. Br J Dermatol. 2012 Mar;166(3):616–623.
- Yan D, Borucki R, Sontheimer RD, Werth VP. Candidate drug replacements for quinacrine in cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Lupus Sci Med. 2020 Oct;7(1):e000430.
Author Response
Thank you so much for your interest in this case.