In addition, patients need to adhere to a dietary regimen and a healthy lifestyle to help prevent further attacks.
Our patient was maintained on colchicine 0.6 mg three times a day and discharged on febuxostat, after which outpatient uric acid levels decreased to normal levels for the first time in four years.
The earliest changes that can be seen in a patient with septic joints include soft tissue swelling & joint space widening or narrowing. Evidence of superimposed osteomyelitis can be seen in the form of periosteal bone reaction & bone destruction.1
Question 3
What is (are) the most common outcome(s) of untreated gout? (Multiple choices may be correct.)
a. sepsis
b. urolithiasis
c. permanent joint destruction
d. bacteremia
e. tophi
Gout is an inflammatory disorder in which uric acid, a toxic metabolic product, accumulates in the form of crystals in the joint spaces. Unabated accumulation of urate can result in tophi that present as papules or nodules in various locations, including tendons, cartilage, osteoarthritis nodes and bursae. The presence of tophi increases the risk of developing joint deformities and secondary osteoarthritis. Following injury, these tophi can become acutely inflamed and even erupt through the skin.
Approximately 20% of patients with chronic gout will develop nephrolithiasis due to both uric acid formation and calcium oxalate deposition.2 This may lead to obstructive nephropathy and subsequent infection.
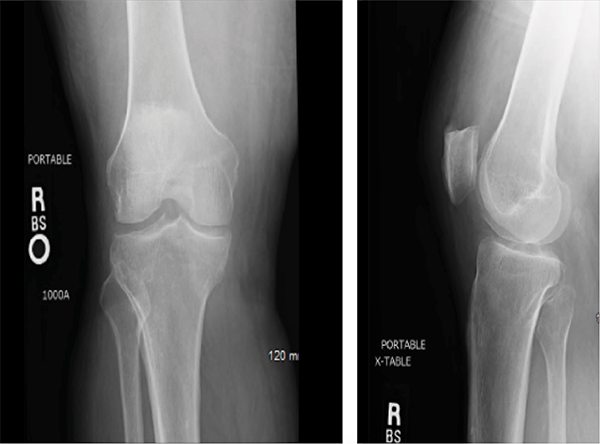
Figures 1 & 2: X-rays of the Right Knee
Question 4
Which of the following can be used to aid in the diagnosis of gout? (Multiple answer choices may be correct.)
a. synovial fluid analysis
b. demonstration of fever and joint pains
c. clinical evidence of gout
d. imaging evidence of urate deposition
e. all of the above
In 2015, the ACR released new criteria for the classification of gout.3 These criteria emphasize physical exam and medical history, with less focus on laboratory results or invasive diagnostic techniques, such as synovial fluid analysis; the sensitivity of joint aspiration can be low, based on the size of the joint space, as well as the experience of the person obtaining and/or examining the sample.
These criteria utilize a point system in which different symptoms and signs are taken into account: distribution of joint involvement, presence of pain and/or erythema, time course of symptomatic episode, clinical evidence of tophi, serum urate levels, synovial fluid analysis, imaging evidence of urate deposition and/or joint damage. Negative points are given for serum urate levels <4 mg/dL and negative synovial findings. A Web-based calculator can be accessed through the ACR’s website.
Question 5
Is it typical to have gout in a patient with known seropositive RA?


