Glucocorticoids
Recommendations: A strong recommendation against glucocorticoid use in patients with SSc as first-line treatment of SARD-ILD was made. However, for patients with ILD related to other SARDs, the conditional recommendation is in favor of glucocorticoid treatment in conjunction with another therapy, usually a traditional immunosuppressive.
The strong recommendation against glucocorticoids as first-line ILD treatment in systemic sclerosis, one of the few strong recommendations in the guideline, is due to the risk of inducing renal crisis in this population. “I think rheumatologists are very familiar with this risk, but people outside the rheumatology community [may] be less so,” says Dr. Bernstein.
In all likelihood, notes Dr. Johnson, clinicians should also avoid glucocorticoids in patients with mixed connective tissue disease who have a scleroderma-dominant phenotype.
Immunomodulators: Initial Treatment
Recommendations: Mycophenolate, rituximab, cyclophosphamide and azathioprine are conditionally recommended as first-line treatments for SARD-ILD, with mycophenolate conditionally recommended above these other agents.
Dr. Johnson notes that guideline developers preferred some agents due to published literature and expert experience, but other agents may be options in specific circumstances. Thus, although these are all potential first-line options, cyclophosphamide and azathioprine may be considered additional options rather than preferred first-line treatment.
In this webinar presented by The Rheumatologist, the ACR and Wiley, Dr. Johnson and Dr. Bernstein discuss the development of the guidelines and the recommendations they contain. Click the image to watch the webinar recording.
Dr. Bernstein notes that many physicians may be reluctant to prescribe cyclophosphamide due to concerns of infection, hemorrhagic cystitis and potential infertility; mycophenolate has a comparatively better side effect profile.
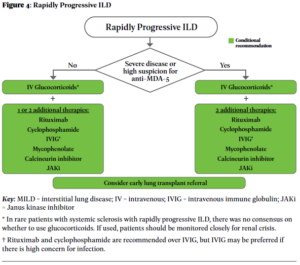
See the full guidelines for additional recommendations with respect to treatment after progression, use of antifibrotics and additional therapies, as well as considerations in rapidly progressing disease.
Ruth Jessen Hickman, MD, a graduate of the Indiana University School of Medicine, is a medical and science writer in Bloomington, Ind.
References
- Johnson SR, Bernstein EJ, Bolster MB, et al. 2023 American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) guideline for the screening and monitoring of interstitial lung disease in people with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024.
- Johnson SR, Bernstein EJ, Bolster MB, et al. 2023 American College of Rheumatology/American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) guideline for the treatment of interstitial lung disease in people with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024.
- van den Bosch L, Luppi F, Ferrara G, Mura M. Immunomodulatory treatment of interstitial lung disease. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2022;16:17534666221117002.
Adapted from an article in the August 2024 issue of The Rheumatologist (Vol. 18, No. 8).