Lastly, patients with positive aPL or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) are also at increased risk for pregnancy complications and should be on low-dose aspirin to prevent pre-eclampsia. Anticoagulation is also recommended for obstetric patients with APS who have had multiple miscarriages or intrauterine demises, or thrombotic APS with a history of thrombosis.
“Hydroxychloroquine is conditionally recommended in patients with APS, given it has mild anticoagulant properties,” she said.
‘The reproductive health guideline recommends patients on mycophenolate also be prescribed a highly effective contraceptive method, such as an IUD, or two other forms of contraception, such as the pill & condoms.’ —Dr. Talabi
Medication Management
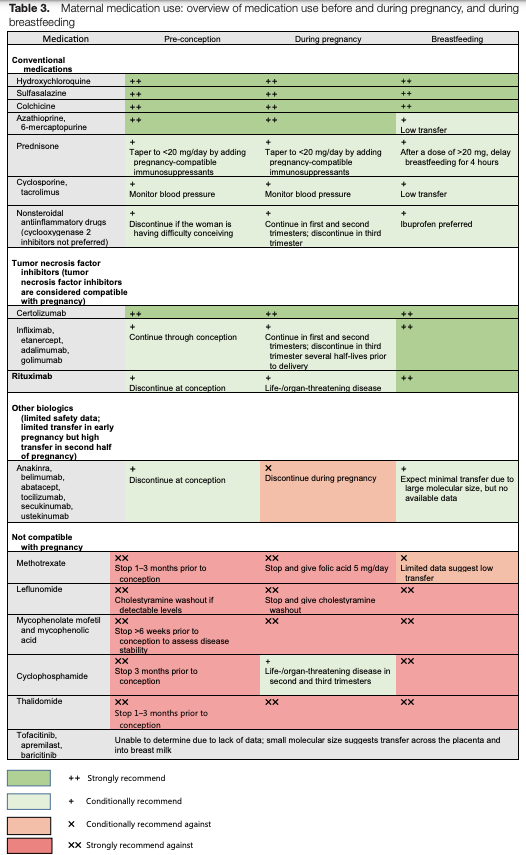
The following medications are safe to use during all phases of pregnancy and lactation: hydroxychloroquine, sulfasalazine, colchicine, azathioprine, prednisone, cyclosporine and tacrolimus. Additionally, all tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors can be used during pregnancy and lactation, although non-certolizumab TNF inhibitors are sometimes discontinued in the third trimester to avoid a potential risk of neonatal immunosuppression.
Medications contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding include methotrexate, leflunomide, mycophenolate, cyclophosphamide and thalidomide. However, cyclophosphamide can be used in the second or third trimester for life- or organ-threatening disease. Small molecule agents, such as Janus kinase inhibitors (jakinibs) or apremilast, are likely to transfer across the placenta and breastmilk. These medications should not be used in pre-conception, during pregnancy or while breastfeeding (see Figure 1, below).
Figure 1: Maternal Medication Use Before & During Pregnancy, & During Breastfeeding1
One new update since the publication of the 2020 guideline was discussed: The FDA does not recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use after 20 weeks of pregnancy because of the risk of oligohydramnios.
Men can safely use most medications during conception. However, cyclophosphamide and thalidomide should be discontinued before attempting to conceive. Because sulfasalazine (SSZ) can reduce sperm counts, semen analysis should be done if a man on SSZ has difficulty conceiving.
Real-World Examples
Next, Lisa Sammaritano, MD, professor of clinical medicine from the Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, and Weill Cornell Medicine, discussed applying the guideline to medication management.
Dr. Sammaritano provided an example of a patient with lupus who was breastfeeding her baby and required initiation of 25 mg of prednisone daily for post-partum flare. For doses of prednisone greater than 20 mg per day, patients should delay breastfeeding—or pump and discard—for four hours after taking the dose. She emphasized considering the addition of steroid-sparing, breastfeeding-compatible medications if prednisone cannot be quickly tapered.