Conclusions
At this juncture several outstanding problems need to be addressed to move the field of GCA forward. Although GCA is the most common form of primary vasculitis among adults in the U.S. and Europe, the cause of this disease is still unknown and its pathogenesis is poorly understood. Vascular inflammation in GCA can have catastrophic consequences, and standardized criteria for accurate diagnosis are lacking. Further, there is no acceptable alternative to treatment with prolonged courses of CS, which are highly toxic in this elderly population of patients.
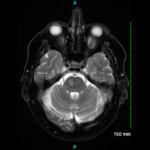
IL-6 signaling inhibition therapy is currently being tested in a large multicenter clinical trial. The exact role of MRA/MRI, CTA and PET with respect to initial diagnosis, evaluation of treatment response, disease activity monitoring, and prediction of disease relapse and late arterial complications is to be defined. For this purpose, vascular imaging outcomes need to be factored into the design of clinical trials.
Sebastian Unizony, MD, is co-director of the Vasculitis and Glomerulonephritis Center in the Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology Division of Massachusetts General Hospital at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
John H. Stone, MD, MPH, is director of clinical rheumatology in the Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology Division of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. He is a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School.
References
- Lee JL, Naguwa SM, Cheema GS, Gershwin ME. The geo-epidemiology of temporal (giant cell) arteritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2008 Oct;35(1–2):88–95.
- Salvarani C, Cantini F, Boiardi L, Hunder GG. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant-cell arteritis. N Engl J Med. 2002 Jul 25;347(4):261–271.
- Hunder GG, Bloch DA, Michel BA, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33(8):1122–1128.
- Kermani TA, Schmidt J, Crowson CS, et al. Utility of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein for the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Jun;41(6):866–871.
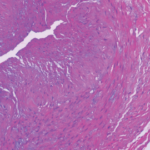
- Narvaez J, Bernad B, Roig-Vilaseca D, et al. Influence of previous corticosteroid therapy on temporal artery biopsy yield in giant cell arteritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Aug;37(1):13–19.
- Prieto-Gonzalez S, Arguis P, Garcia-Martinez A, et al. Large vessel involvement in biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis: Prospective study in 40 newly diagnosed patients using CT angiography. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012 July;71(7):1170–1176.
- Meller J, Strutz F, Siefker U, et al. Early diagnosis and follow-up of aortitis with [(18)F]FDG PET and MRI. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003 May;30(5):730–736.
- Grayson PC, Maksimowicz-McKinnon K, Clark TM, et al. Distribution of arterial lesions in Takayasu’s arteritis and giant cell arteritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012 Aug;71(8):1329–1334.
- Blockmans D, de Ceuninck L, Vanderschueren S, et al. Repetitive 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in giant cell arteritis: A prospective study of 35 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Feb15;55(1):131–137.
- Besson FL, Parienti JJ, Bienvenu B, et al. Diagnostic performance of (1)(8)F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in giant cell arteritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011 Sep;38(9):1764–1772.
- Proven A, Gabriel SE, Orces C, et al. Glucocorticoid therapy in giant cell arteritis: Duration and adverse outcomes. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Oct 15;49(5):703–708.
- Deng J, Younge BR, Olshen RA, et al. Th17 and Th1 T-cell responses in giant cell arteritis. Circulation. 2010 Feb 23;121(7):906–915.
- Terrier B, Geri G, Chaara W, et al. Interleukin-21 modulates Th1 and Th17 responses in giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Jun;64(6):2001–2011.
- Samson M, Audia S, Fraszczak J, et al. Th1 and Th17 lymphocytes expressing CD161 are implicated in giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica pathogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Nov;64(11):3788–3798.
- Weyand CM, Fulbright JW, Hunder GG, et al. Treatment of giant cell arteritis: Interleukin-6 as a biologic marker of disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 May;43(5):1041–1048.
- Unizony S, Stone JH, Stone JR. New treatment strategies in large-vessel vasculitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013 Jan;25(1):3–9.
- Unizony SH, Dasgupta B, Fisheleva E, et al. Design of the tocilizumab in giant cell arteritis trial. Int J Rheumatol. 2013; 2013:912562.