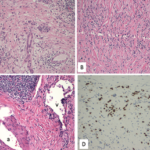
Frequent complications of MD include AIP, retroperitoneal fibrosis and TIN with extraglandular involvement. Therefore, systemic examination and a fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) scan should be performed because multiple organ involvement might be present at initial diagnosis (see Fig. 1, and Fig. 2).38
First-line treatment is steroids with rapid disease response, but frequent flares can occur following discontinuation of glucocorticoid treatment.
Disease Pathophysiology
The presence of IgG4-positive plasma cells in the affected tissue and the fact that B cell depletion with rituximab (RTX) is effective in treatment suggest the importance of B-lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of IgG4-RD.39,40 Plasmablasts defined by cell surface expression of CD19, CD27 and CD38 (but negative for CD20) are elevated in the peripheral blood of patients with IgG4-RD correlating with disease activity. Because these plasmablasts demonstrate oligoclonal expansion and express IgG4, a specific antigen-driven immune response might be present in IgG4-RD.41,42
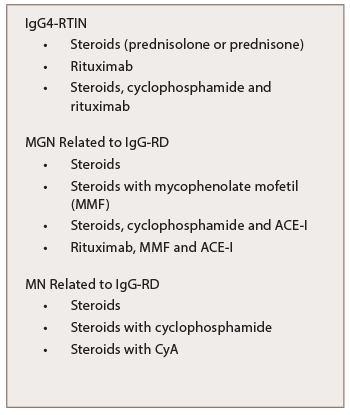
Table 7: Treatment of IgG-RKD
A Type 2 helper T cell (Th2)-driven immunological mechanism has been suggested in the pathogenesis of IgG4-RD as well.43 A clonally-expanded population of CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood and fibrotic lesions of IgG4-RD patients suggest these cells are important in the disease pathogenesis by activating B cells.44 The Th2 cytokine IL-13 and the T-regulatory-associated cytokine transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) are thought to activate fibroblasts and cause fibrosis, while the cytokines IL-4 and IL-10 might promote class-switching of IgG antibodies to IgG4 and differentiation of B cells into plasma cells. Polarized T cells possibly drive the storiform fibrosis and obliterative phlebitis observed in IgG4-RD. A separate T follicular helper cell response might generate the IgG4 phenotype.45
Memory CD4+ T cells produced by the continuous antigen presentation of B cells might explain the clinical improvement in B cell depletion. A parallel T follicular helper cell response, activated either by the same antigen or an event triggered by fibrosis, might induce the production of germinal centers within lymph nodes and generate plasmablasts that secrete IgG4. The latest studies have shown M2 macrophages activated by the cytokines such as IL-4 or IL-13 may also take part in the fibrosing process. Toll-like receptors on macrophages participate in class-switch recombination through B cell activating factor and could lead to further activation and proliferation of IgG4-positive B cells.46
Treatment
The first-line treatment is prednisolone at 0.6 mg/kg/day, or 30–40 mg/day of prednisolone as the initial dose to induce remission in type 1 AIP. Continue this dose for two to four weeks, and then gradually taper by 5 mg every one to two weeks to a maintenance dose of 5–10 mg/day.