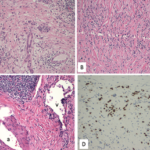
First-line treatment is glucocorticoids, which induce a rapid disease response, but frequent flares can occur following discontinuation of glucocorticoid treatment. In cases of recurrent disease or disease refractory to steroids the addition of immunosuppressants, such as rituximab, azathioprine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil or cyclophosphamide, is recommended. Although CD20-targeted B cell depletion is a promising treatment, plasmablast-targeted treatment with monoclonal antibodies and novel therapies against CD4+ CTLs may be more specific and effective future treatment approaches for IgG4-RD. R
 Despina Michailidou, MD, PhD, is a first-year rheumatology fellow at the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md. She obtained her MD from the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens in Greece. She received her PhD from the Goethe University of Frankfurt in Germany. She completed her residency in internal medicine at Yale New Haven Health System.
Despina Michailidou, MD, PhD, is a first-year rheumatology fellow at the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md. She obtained her MD from the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens in Greece. She received her PhD from the Goethe University of Frankfurt in Germany. She completed her residency in internal medicine at Yale New Haven Health System.
 Paul J. Cohen, MD, chairs the Bridgeport Hospital Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine in Bridgeport, Conn. He spends most of his time in general surgical pathology and has a specialty interest in cardiovascular pathology. He’s an assistant professor of pathology at Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Conn. He’s also the director of the Yale Pathology residency program at Bridgeport Hospital.
Paul J. Cohen, MD, chairs the Bridgeport Hospital Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine in Bridgeport, Conn. He spends most of his time in general surgical pathology and has a specialty interest in cardiovascular pathology. He’s an assistant professor of pathology at Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Conn. He’s also the director of the Yale Pathology residency program at Bridgeport Hospital.
Acknowledgment: This review was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases of the National Institutes of Health.
References
- Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012 Feb 9;366(6):539–551.
- Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, et al. A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): General concept and details. Mod Rheumatol. 2012 Feb;22(1):1–14.
- Saeki T, Nishi S, Imai N, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of patients with IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2010 Nov;78(10):1016–1023.
- Deshpande V, Chicano S, Finkelberg D, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis: A systemic immune complex mediated disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006 Dec;30(12):1537–1545.
- Alexander MP, Larsen CP, Gibson IW, et al. Membranous glomerulonephritis is a manifestation of IgG4-related disease. Kidney Int. 2013 Mar;83(3):455–462.
- Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 2012 Feb;22(1):21–30.
- Kawano M, Saeki T, Nakashima H, et al. Proposal for diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011 Oct;15(5):615–626.
- Yamaguchi Y, Kanetsuna Y, Honda K, et al. Characteristic tubulointerstitial nephritis in IgG4-related disease. Hum Pathol. 2012 Apr;43(4):536–549.
- Okazaki K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T, et al. Clinical diagnostic criteria of autoimmune pancreatitis: Revised proposal. J Gastroenterol. 2006 Jul;41(7):626–631.
- Shoji S, Nakano M, Usui Y. IgG4-related inflammatory pseudotumor of the kidney. Int J Urol. 2010 Apr;17(4):389–390.
- Khosroshahi A, Stone JH. A clinical overview of IgG4-related systemic disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011 Jan;23(1):57–66.
- Cornell LD, Chicano SL, Deshpande V, et al. Pseudotumors due to IgG4 immune-complex tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with autoimmune pancreatocentric disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007 Oct;31(10):1586–1597.
- Fukuhara H, Taniguchi Y, Matsumoto M, et al. IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis accompanied with cystic formation. BMC Urol. 2014 Jul 20;14:54.
- Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012 Sep;25(9):1181–1192.
- 15. Sharma SG, Vlase HL, D’Agati VD. IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis with plasma cell-rich renal arteritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013 Apr;61(4):638–643.
- Tsubata Y, Akiyama F, Oya T, et al. IgG4-related chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis without autoimmune pancreatitis and the time course of renal function. Intern Med. 2010;49(15):1593–1598.
- Saeki T, Kawano M. IgG4-related kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2014 Feb;85(2):251–257.
- Stone JH. IgG4: A tantalizing link between causes of membranous glomerulonephritis and systemic disease. Kidney Int. 2013 Mar;83(3):348–350.
- Morimoto J, Hasegawa Y, Fukushima H, et al. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis-like glomerular disease and concurrent tubulointerstitial nephritis complicating IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis. Intern Med. 2009;48(3):157–162.
- Cravedi P, Abbate M, Gagliardini E, et al. Membranous nephropathy associated with IgG4-related disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011 Aug;58(2):272–275.
- Fervenza FC, Downer G, Beck LH Jr., et al. IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis with membranous nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011 Aug;58(2):320–324.
- Li J, Qu Z, Zhang YM, et al. [Clinical significance of detection of plasma and urine IgG4 in idiopathic membranous nephropathy]. Beijing Da Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010 Dec 18;42(6):671–674.
- Li XL, Yan TK, Li HF, et al. IgG4-related membranous nephropathy with high blood and low urine IgG4/IgG ratio: A case report and review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol. 2014 Jan;33(1):145–148.
- Beck LH Jr., Bonegio RG, Lambeau G, et al. M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2009 Jul;361(1):11–21.
- Imai H, Hamai K, Komatsuda A, et al. IgG subclasses in patients with membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, membranous nephropathy and lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 1997 Jan;51(1):270–276.
- Debiec H, Ronco P. PLA2R autoantibodies and PLA2R glomerular deposits in membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2011 Feb 17;364(7):689–690.
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Ochi Y, et al. Hydronephrosis associated with retroperitoneal fibrosis and sclerosing pancreatitis. Lancet. 2002 Apr 20;359(9315):1403–1404.
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. New Engl J Med. 2001 Mar 8;344(10):732–738.
- Van Moerkercke W, Verhamme M, Meeus G, et al. A case of IgG4-related sclerosing disease with retroperitoneal fibrosis, autoimmune pancreatitis and bilateral focal nephritis. Pancreas. 2009 Oct;38(7):825–832.
- Cornell LD. IgG4-related kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012 May;21(3):279–288.
- Sarles H, Sarles JC, Camatte R, et al. Observations on 205 confirmed cases of acute pancreatitis, recurring pancreatitis and chronic pancreatitis. Gut. 1965 Dec;6(6):545–559.
- Kim KP, Kim MH, Kim JC, et al. Diagnostic criteria for autoimmune chronic pancreatitis revisited. World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Apr 28;12(16):2487–2496.
- Kwon S, Kim MH, Choi EK. The diagnostic criteria for autoimmune chronic pancreatitis: It is time to make a consensus. Pancreas. 2007 Apr;34(3):279–286.
- Chari ST, Smyrk TC, Levy MJ, et al. Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis: The Mayo Clinic experience. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006 Aug;4(8):1010–1016.
- Gardner TB, Chari ST. Autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2008 Jun;37(2):439–460.
- Yamamoto M, Harada S, Ohara M, et al. Clinical and pathological differences between Mikulicz’s disease and Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005 Feb;44(2):227–234.
- Mavragani CP, Fragoulis GE, Rontogianni D, et al. Elevated IgG4 serum levels among primary Sjögren’s syndrome patients: Do they unmask underlying IgG4-related disease? Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014 May;66(5):773–777.
- Suga K, Kawakami Y, Hiyama A, et al. F-18 FDG PET-CT findings in Mikulicz disease and systemic involvement of IgG4-related lesions. Clin Nucl Med. 2009 Mar;34(3):164–167.
- Umehara H, Nakajima A, Nakamura T, et al. IgG4-related disease and its pathogenesis-cross-talk between innate and acquired immunity. Int Immunol. 2014 Nov;26(11):585–595.
- Khosroshahi A, Bloch DB, Deshpande V, et al. Rituximab therapy leads to rapid decline of serum IgG4 levels and prompt clinical improvement in IgG4-related systemic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Jun;62(6):1755–1762.
- Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Della-Torre E, et al. De novo oligoclonal expansions of circulating plasmablasts in active and relapsing IgG4-related disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014 Sep;134(3):679–687.
- Wallace ZS, Mattoo H, Carruthers M, et al. Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Jan;74(1):190–195.
- Lighaam LC, Aalberse RC, Rispens T. IgG4-related fibrotic diseases from an immunological perspective: Regulators out of control? Int J Rheumatol. 2012;2012:789164.
- Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Maehara T, et al. Clonal expansion of CD4(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with IgG4-related disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Sep;138(3):825–838.
- Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Shinomura Y. Mechanisms and assessment of IgG4-related disease: Lessons for the rheumatologist. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014 Mar;10(3):148–159.
- Watanabe T, Yamashita K, Fujikawa S, et al. Involvement of activation of toll-like receptors and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors in enhanced IgG4 responses in autoimmune pancreatitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Mar;64(3):914–924.
- Brito-Zeron P, Kostov B, Bosch X, et al. Therapeutic approach to IgG4-related disease: A systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jun;95(26):e4002.
- Khosroshahi A, Stone JH. Treatment approaches to IgG4-related systemic disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011 Jan;23(1):67–71.
- Saeki T, Kawano M, Mizushima I, et al. The clinical course of patients with IgG4-related kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013 Oct;84(4):826–833.
- Quattrocchio G, Roccatello D. IgG4-related nephropathy. J Nephrol. 2016 Aug;29(4):487–493.
- Kanda H, Koya J, Uozaki H, et al. Membranous nephropathy with repeated flares in IgG4-related disease. Clin Kidney J. 2013 Apr;6(2):204–207.
- Ghazale A, Chari ST, Zhang L, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis: Clinical profile and response to therapy. Gastroenterology. 2008 Mar;134(3):706–715.
- Ebbo M, Daniel L, Pavic M, et al. IgG4-related systemic disease: Features and treatment response in a French cohort: Results of a multicenter registry. Medicine (Baltimore). 2012 Jan;91(1):49–56.
- Kawano M, Mizushima I, Yamaguchi Y, et al. Immunohistochemical characteristics of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis: Detailed analysis of 20 Japanese cases. Int J Rheumatol. 2012;2012:609795.
- Chu SY, Yeter K, Kotha R, et al. Suppression of rheumatoid arthritis B cells by XmAb5871, an anti-CD19 antibody that coengages B cell antigen receptor complex and Fcgamma receptor IIb inhibitory receptor. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 May;66(5):1153–1164.
- Perugino CA, Stone JH. Treatment of IgG4-related disease: Current and future approaches. Z Rheumatol. 2016 Sep;75(7):681–686.