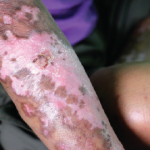
An unmet need still exists for therapies that may be more effective than methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, intravenous immunoglobulin & cyclophosphamide in treating skin disease in scleroderma.
Treatment Options
With respect to treatment options, Dr. Hummers’ clinical practice is to evaluate the domains involved (e.g., skin, interstitial lung disease, myositis, arthritis) and treat accordingly. She noted that, although nintedanib and tocilizumab are now approved by the U.S. Food & Drug Administration for the treatment of scleroderma-associated interstitial lung disease, neither agent has shown benefit in improving cutaneous involvement.
Lenabasum, an oral, non-immunosuppressive preferential cannabinoid-2 agonist, was tested in the RESOLVE-1 trial after showing promise in a phase 2 study. In a 52-week randomized clinical trial, Spiera et al. enrolled 365 patients with early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (with 84% of patients on background therapy) and randomized them to 5 mg or 20 mg of lenabasum twice daily or placebo.
The authors found no difference in the primary or secondary key endpoints between the study medication (lenabasum 20 mg twice daily) and placebo.1 These findings indicate that an unmet need still exists for therapies that may be more effective than methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and cyclophosphamide in treating skin disease in scleroderma.
Raynaud’s Phenomenon
Dr. Hummers next discussed Raynaud’s phenomenon, including the features that make secondary causes more likely, such as onset at older age, abnormal nailfold capillaries, positivity for scleroderma-associated autoantibodies, etc., and the importance of screening for pulmonary hypertension with annual echocardiogram and pulmonary function testing in these patients at higher risk.
Non-pharmacologic treatment for Raynaud’s includes keeping hands, feet and the central body warm; avoiding stress and quitting smoking; and avoiding common precipitants of the condition, such as caffeine and beta blockers. For patients with persistent symptoms, sustained-release dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers are indicated; if low baseline blood pressure is present, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, pentoxifylline and statins may be potential options. For severe acute or recurrent digital ischemia, prostacyclin analogs or botulinum toxin injection can be of help.
Renal Crisis
Dr. Hummers concluded the lecture discussing two important topics: scleroderma renal crisis and gastrointestinal manifestations of scleroderma. Risk factors for renal crisis include diffuse, rapidly progressive cutaneous disease, African American race, positivity for antibodies to RNA polymerase III, and use of corticosteroids (particularly >15 mg of prednisone per day). With only a 65% five-year survival in patients who suffer this complication, screening for the condition with daily blood pressure measurements is critical, and any new onset of hypertension (particularly blood pressure >140/90 lasting for more than 24 hours) should prompt workup and likely hospital admission.