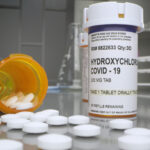
NEW YORK, June 4 (Reuters)—Three of the authors of an influential article that found hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) increased the risk of death in COVID-19 patients retracted the study, citing concerns about the quality of the data behind it.
The anti-malarial drug has been controversial in part due to support from U.S. President Donald Trump, as well as implications of the study published in British medical journal the Lancet last month.1
The three authors said Surgisphere, the company that provided the data, would not transfer the full dataset for an independent review and that they “can no longer vouch for the veracity of the primary data sources.”
The fourth author of the study, Dr. Sapan Desai, the CEO of Surgisphere, declined to comment on the retraction.
The observational study published in the Lancet on May 22 looked at 96,000 hospitalized COVID-19 patients, some treated with the decades-old malaria drug. It claimed that those treated with HCQ or the related chloroquine had higher risk of death and heart rhythm problems than patients who were not given the medicines.
Several clinical trials were put on hold after the study was published. The World Health Organization, which paused HCQ trials after The Lancet study was released, said it was ready to resume trials.
Many scientists voiced concern about the study. Nearly 150 doctors signed an open letter to The Lancet last week calling the article’s conclusions into question and asking to make public the peer review comments that preceded publication.
“I did not do enough to ensure that the data source was appropriate for this use,” the study’s lead author, Harvard Medical School Professor Mandeep Mehra, says in a statement. “For that, and for all the disruptions—oth directly and indirectly—I am truly sorry.”
Surgisphere was not immediately available for comment.
The Lancet in a statement says, “There are many outstanding questions about Surgisphere and the data that were allegedly included in this study.”
(Reporting by Michael Erman and Peter Henderson. Editing by Tom Brown and Leslie Adler.)
Reference
- Mehra MR, Desai SS, Ruschitzka F, et al. Hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine with or without a macrolide for treatment of COVID-19: A multinational registry analysis. The Lancet. 2020 May 22.