Discussion
The authors acknowledged that patients who received litifilimab may be at increased risk of infections. In their study, they identified three cases of oral herpes infection and one case of herpes zoster infection. Additionally, one case of herpes zoster meningitis occurred four months after the patient received their last dose of litifilimab. The investigators also documented three cases of hypersensitivity.
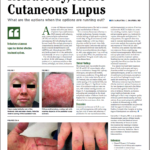
Absent approved treatments for cutaneous lupus erythematosus, rheumatologists typically treat patients with topical glucocorticoids and antimalarial medications.3 Unfortunately, limited evidence exists regarding the benefit of glucocorticoids, and a 2017 meta-analysis found that responses to antimalarial medications on skin manifestations may vary widely.4
“This has been an interesting study because it really focuses on patients with unmet needs,” says Nathalie Franchimont, MD, PhD, chief medical officer for Nimbus Therapeutics in Cambridge, Ma., and corresponding author for the paper.
The published results come from part B of a larger study. The investigators published results from part A of the study in September.5 The second analysis found that litifilimab was associated with a greater reduction in the number of swollen and tender joints from baseline than placebo over a period of 24 weeks.
The team has begun two concurrent phase 3 clinical trials (TOPAZ-1 and TOPAZ-2), which are designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of a year of treatment with litifilimab compared with placebo in patients with active SLE. Trial participants will also receive background lupus standard of care therapy. TOPAZ-1 and TOPAZ-2 are enrolling up to 540 participants at multiple sites worldwide.
Lara C. Pullen, PhD, is a medical writer based in the Chicago area.
References
- Werth VP, Furie RA, Romero-Diaz J, et al. Trial of anti-BDCA2 antibody litifilimab for cutaneous lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2022 Jul 28;387(4):321–331.
- Gronhagen CM, Fored CM, Granath F, et al. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus and the association with systemic lupus erythematosus: A population-based cohort of 1088 patients in Sweden. Br J Dermatol. 2011 Jun;164(6):1335–1341.
- Kuhn A, Aberer E, Bata-Csorgo Z, et al. S2k guideline for treatment of cutaneous lupus erythematosus – guided by the European Dermatology Forum (EDF) in cooperation with the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017 Mar;31(3):389–404.
- Chasset F, Bouaziz J-D, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, et al. Efficacy and comparison of antimalarials in cutaneous lupus erythematosus subtypes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2017 Jul;177(1):188–196.
- Furie RA, van Vollenhoven RF, Kalunian K, et al. Trial of anti-BDCA2 antibody litifilimab for systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2022 Sep 8;387(10):894–904.