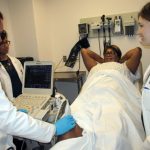
In a session on a current ACR project on musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSUS), Gurjit Kaeley, MBBS, RhMSUS, MRCP, division chief, professor of medicine, fellowship program director and program director for musculoskeletal ultrasound at the University of Florida College of Medicine, Jacksonville, will present information on proposed guidance related to rheumatoid arthritis. The ACR places a high…