- Do not start golimumab during an active infection. If an infection develops, monitor carefully and stop golimumab if the infection becomes serious.
- For patients who develop a systemic illness on golimumab, consider empiric anti-fungal therapy for those who reside in or travel to regions where mycoses, such as histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis or blastomycosis, are endemic.
- HBV many occur. Monitor HBV carriers during and several months after therapy. If reactivation occurs, stop golimumab and begin anti-viral therapy.
- The incidence of lymphoma was seen more often than in the general U.S. population. Cases of other malignancies have been observed among patients receiving a TNFi.
- Heart failure, worsening, or new onset, may occur. Stop golimumab if new or worsening symptoms occur.
- Demyelinating disease, exacerbation or new onset, may occur.
- Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, may occur.
- Lupus-like syndrome—stop golimumab if the syndrome develops.
Dosage & Administration
Golimumab is administered by SQ injection. The recommended dose is 50 mg once a month in combination with MTX.
Commentary
The FDA approval of golimumab injection was based on the results of three multi-center, randomized, double-blind, controlled trials that enrolled more than 1,500 patients. The most common adverse reactions (>5%) were upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis and injection site reactions.
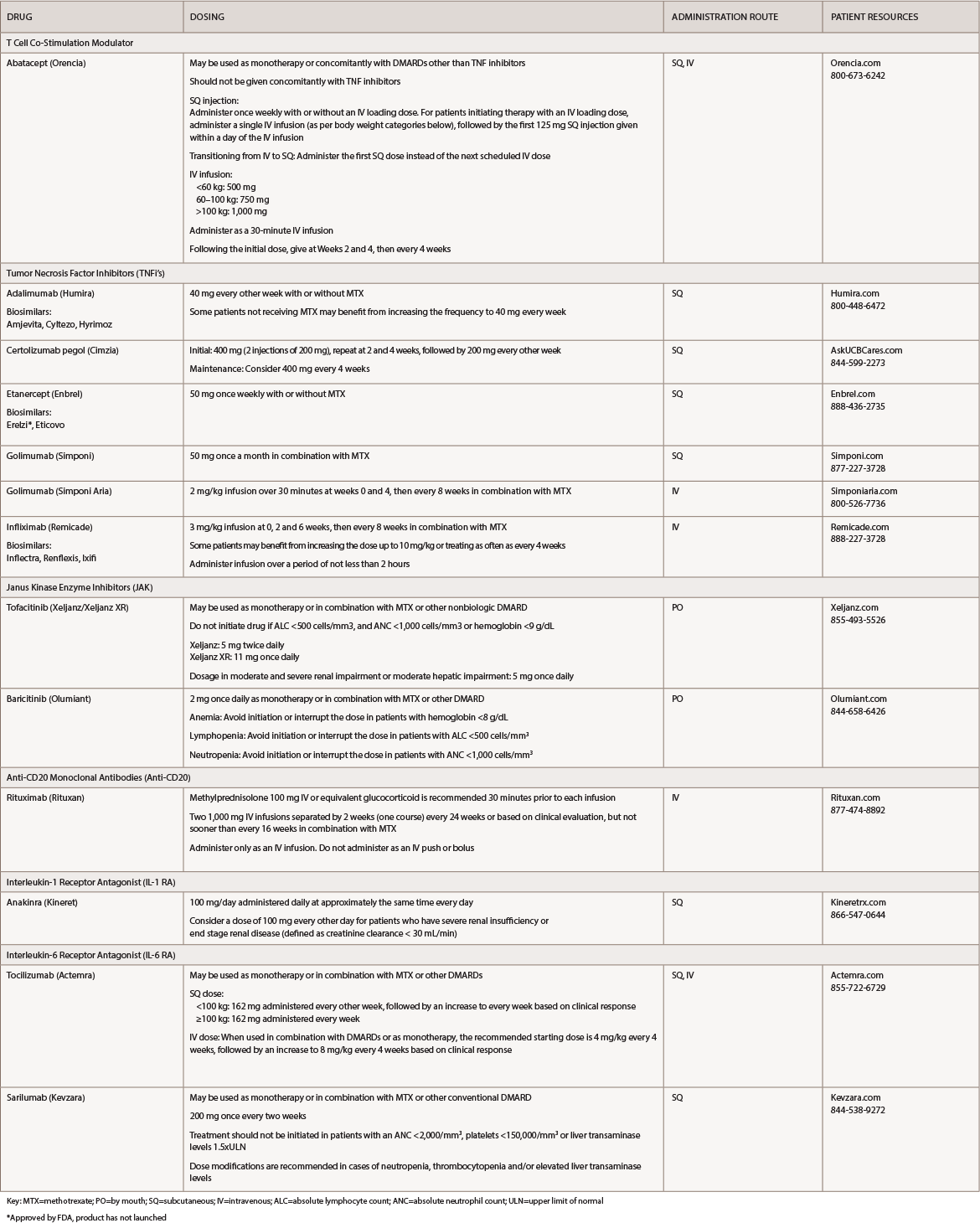
(click for larger image) Table 1: Rheumatoid Arthritis Medications at a Glance
Key: MTX=methotrexate; PO=by mouth; SQ=subcutaneous; IV=intravenous; ALC=absolute lymphocyte count; ANC=absolute neutrophil count; ULN=upper limit of normal
*Approved by FDA, product has not launched
Golimumab (Simponi Aria):18 infusion
Drug class: DMARD, TNFi
Boxed warning: Refer to *ISI (p. 14)
Warnings & Precautions: Refer to *Simponi
Dosage & Administration
Golimumab is administered by IV infusion. The recommended dose is 2 mg/kg over 30 minutes at Weeks 0 and 4, then every eight weeks in combination with MTX.
Commentary
The FDA approval of golimumab injection for IV use was based on results from a clinical trial that enrolled nearly 600 patients. The trial showed the drug significantly improved the signs and symptoms of RA, improved physical function and slowed the progression of structural damage. The most common adverse reactions (≥3%) were upper respiratory tract infection, increased alanine aminotransferase, viral infection, increased aspartate aminotransferase, decreased neutrophil count, bronchitis, hypertension and rash.
Infliximab (Remicade):19 infusion
Biosimilar(s): infliximab-dyyb (Inflectra),20 infliximab-abda (Renflexis),21 infliximab-qbtx (Ixifi)22
Drug class: DMARD, TNFi
Boxed warning: Refer to *ISI (p. 14) and
- Fatal hepatosplenic T cell lymphoma (HSTCL) have been reported in patients treated with TNFi’s, post-marketing. All infliximab cases occurred in IBD patients, who were mostly adolescent or young adult males. All had received azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine concomitantly with infliximab at or prior to diagnosis.
Warnings & Precautions