- Fatal infusion-related reactions within 24 hours of rituximab infusion; approximately 80% of fatal reactions occurred with the first infusion. Monitor patients, and discontinue infusion for severe reactions.
- Severe mucocutaneous reactions have occurred, some with fatal outcomes.
- HBV reactivation, in some cases resulting in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure and death, has occurred.
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) resulting in death has occurred.
Warnings & Precautions
- Infections: Withhold rituximab, and institute appropriate anti-infective therapy.
- Cardiac adverse reactions: Discontinue infusions in case of serious or life-threatening events.
- Renal toxicity: Discontinue in patients with rising serum creatinine or oliguria.
- Bowel obstruction and perforation: Consider and evaluate for abdominal pain, vomiting or related symptoms.
- Immunizations: Live virus vaccinations prior to or during rituximab treatment are not recommended.
- Embryo-fetal toxicity: Can cause neonatal harm. Advise patients of the potential risk to neonates and use of effective contraception.
Dosage & Administration
Rituximab is administered only as an IV infusion. The dose of rituximab in combination with MTX is two 1,000 mg IV infusions separated by two weeks (one course) every 24 weeks or based on clinical evaluation, but not sooner than every 16 weeks. Administration of 100 mg of methylprednisolone via IV or equivalent glucocorticoid is recommended 30 minutes prior to each infusion.
Commentary
The FDA approved rituximab based on a clinical trial that enrolled 465 patients with moderate to severe RA. A total of 55% of the patients treated with the higher dose rituximab regimen showed a 20% or better improvement after six months, compared with 54% of patients on the low-dose regimen and 28% of patients taking a placebo. The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) were upper respiratory tract infections, nasopharyngitis, urinary tract infections, bronchitis, infusion-related reactions, serious infections and cardiovascular events.
Anakinra (Kineret):28 injection
Drug class: IL-1 RA, DMARD
Warnings & Precautions
- Discontinue use if serious infection develops.
- Avoid the use of anakinra in combination with TNF inhibitors.
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema, have been reported.
- The impact of treatment with anakinra on active and/or chronic infections and the development of malignancies is not known.
- Live vaccines should not be given concurrently with anakinra.
- Neutrophil counts should be assessed prior to initiating anakinra treatment, and while receiving anakinra, monthly for three months, and thereafter quarterly for a period up to one year.
Dosage & Administration
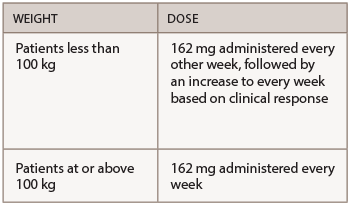
Anakinra is administered by SQ injection. The recommended dose of anakinra is 100 mg/day administered daily at approximately the same time each day. For RA patients who have severe renal insufficiency or end-stage renal disease (defined as creatinine clearance <30 mL/min), healthcare providers should consider a dose of 100 mg of anakinra administered every other day.
Commentary
Anakinra is the first selective antagonist of interleukin (IL) 1. In clinical trials, most patients experienced a decrease in inflammation and pain by Week 13 of treatment. Thirty-eight percent of patients treated with anakinra met ACR20 criteria for improvement compared with 22% of patients receiving placebo. The most common adverse reactions (≥5%) were injection site reaction, worsening of RA, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, nausea, diarrhea, sinusitis, arthralgia, flu like-symptoms and abdominal pain.
Tocilizumab (Actemra):29 injection, infusion
 Drug class: IL-6 RA, DMARD
Drug class: IL-6 RA, DMARD
Boxed Warning