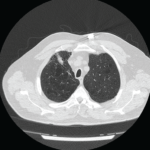
The data supporting a role for the lungs in the pathogenesis of RA have moved beyond antibody production. A study from Colorado compared the spirometry and lung CT imaging findings in a sample of patients with confirmed RA of less than one year’s duration to a group of ACPA-positive individuals lacking clinical RA. Investigators found similar findings of chronic lung inflammation in both groups.8
Taking these data one step further, using mass-spectrometry-based proteomics, a Swedish group studied bronchial and synovial biopsy specimens from a small group of patients with RA and found identical citrullinated peptides present in both tissues, providing further support for a link between lungs and joints in RA.9
This all reminds me of another patient I met many years ago who drove down from the woods of northern New Hampshire to be evaluated for what his country doctor called lung arthritis. Upon hearing the term, I chuckled and carefully explained how his doctor was clearly mistaken and confused about RA. Now I realize that I was the one who was confused!
 Simon M. Helfgott, MD, is associate professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology, Immunology and Allergy at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
Simon M. Helfgott, MD, is associate professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology, Immunology and Allergy at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
References
- Helfgott SM, Kratz A. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital: Case 19-2001—A 50-year-old man with fever and joint pain. N Engl J Med. 2001 Jun 21;344(25):1929–1935.
- Hoffbrand BI, Beck ER. ‘Unexplained’ dyspnoea and shrinking lungs in systemic lupus erythematosus. Br Med J. 1965 May 15;1(5445):1273–1277.
- Pullen LC. A new syndrome of autoimmunity: COPA mutation implicated in lung disease & arthritis. The Rheumatologist. 2015 Jun; 9(6):53–54.
- Watkin LB, Jessen B, Wiszniewski W, et al. COPA mutations impair ER-Golgi transport and cause hereditary autoimmune-mediated lung disease and arthritis. Nat Genet. 2015 Apr 20;47(6):654–660.
- Miall WE, Caplan A, Cochrane AL, et al. An epidemiological study of rheumatoid arthritis associated with characteristic chest X-ray appearances in coal workers. Br Med J. 1953 Dec 5;2(4848):1231–1236.
- Klareskog L, Stolt P, Lundberg K, et al. A new model for an etiology of rheumatoid arthritis: Smoking may trigger HLA–DR (shared epitope)–restricted immune reactions to autoantigens modified by citrullination. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:38–46.
- Quirke A-M, Perry E, Cartwright A, et al. Bronchiectasis is a model for chronic bacterial infection inducing autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2015;67(9):2335–2342.
- Demoruelle MK, Weisman MH, Simonian PL, et al. Brief report: Airways abnormalities and rheumatoid arthritis-related autoantibodies in subjects without arthritis: Early injury or initiating site of autoimmunity? Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Jun;64(6):1756–1761.
- Ytterberg AJ, Joshua V, Reynisdottir G, et al. Shared immunological targets in the lungs and joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Identification and validation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Sep;74:1772–1777.