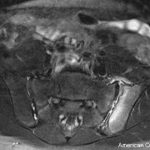
In a study of patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA), researchers found that the cytokine IL-17A may play a role in the pain associated with the disease. Specifically, decreased serum levels of vitamin D3 may contribute to OA pain via the regulation of immune responses…