Take the challenge. D. When an infusion is ordered by the provider, there should be a signed order from the provider. If a prior authorization is needed, it should be obtained, with the number of infusions, along with the start and end dates of the authorization. Also, a prior authorization does not guarantee reimbursement; an…
Coding Corner Questions: An Office Personnel Quiz
A 65-year-old male patient diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis at multiple sites without rheumatoid factor has been ordered to have infliximab infusions. What should support staff do to ensure this procedure can be given to the patient? Make sure there is a signed order from the provider Make sure a prior authorization is obtained Make sure…

The Latest Advances in Sjögren’s, Scleroderma, RA, Gout & More
ATLANTA—At the ACR/ARP 2019 Annual Meeting, several widely renowned experts across an array of specialty subjects provided a comprehensive and compelling review of advances in the understanding, diagnosis and treatment of a number of rheumatologic conditions. Sjögren’s Syndrome Frederick Vivino, MD, FACR, chief of rheumatology at Penn Presbyterian Medical Center and professor of clinical medicine…
New Study Identifies How Big a Role Diet Plays in Hyperuricemia
Living like a king has its price. And while kings and queens are primarily something of yesteryear, the vast majority of those living in reasonably wealthy nations can now live like kings. Now, back to that price. Gout, once known as the disease of kings, has been around at least since the time of the…
New Study Sheds Light on Deficiency of Adenosine Deaminase 2 (DADA2)
Since it was first described, the spectrum of disease caused by deficiency of adenosine deaminase 2 (DADA2) has been broadening. Features described include systemic vascular and inflammatory features and recurrent stroke, which overlap with childhood-onset polyarteritis nodosa (PAN). Previous data show that DADA2 has extensive genotypic and phenotypic variation.1 Results from a recently published study…
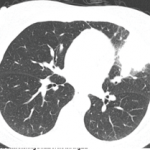
Case Report: A Patient’s Clubbing & Arthralgias Resist Diagnosis
A 59-year-old woman presented to our rheumatology clinic with a six-month history of a symmetric polyarthritis. She initially experienced pain in both knees. As time progressed, she began to notice pain in her ankles, hips, shoulders, hands and feet. She experienced joint stiffness lasting for more than 30 minutes every morning. She also described worsening…
Not All Rheumatoid Factor-Positive Tests Mean RA
Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL) is an aggressive, peripheral T cell, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma with an incidence of 0.05 cases per 100,000 person-years in the U.S., and it typically manifests in adults older than 60 years.1,2 AITL was previously known as angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy with dysproteinemia, immunoblastic lymphadenopathy or lymphogranulomatosis X, due to the hypothesis that the…
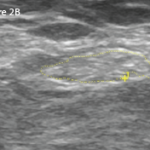
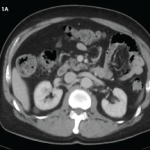
Case Report: Ultrasound Reveals Cause of Post-Arthroplasty Knee Pain
A 65-year-old woman was referred by an orthopedist to a rheumatologist for left knee pain. Previously, in 2014, she underwent left total knee arthroplasty (TKA) for severe osteoarthritis in a different institution. Following the procedure, she experienced severe chronic anterolateral knee pain at rest, exacerbated by walking. Because she was rendered wheelchair bound and required…
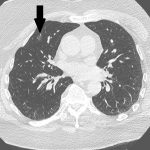
2 Patients on Different DMARDs Experience Different COVID-19 Disease Courses
In March 2020, an elderly married couple living on Long Island, N.Y., presented to our emergency department with symptoms suspicious for COVID-19 infection. The wife, a-76-year-old woman, presented with complaints of subjective fevers, minimal dry cough and headaches of one-week duration. She denied having any chills, rhinorrhea, diarrhea, abdominal pain or shortness of breath. Two…

Industrial Fine Particulate Air Pollution Linked to Increased ACPA Positivity
Researchers investigating the effects of air pollutants on a biomarker for rheumatic autoimmune diseases have found a significant correlation between anti-citrullinated protein antibody positivity in the general population and exposure to industrial fine particulate matter…
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- …
- 336
- Next Page »