Based on a request by the ACR Insurance Subcommittee, off-label use of mycophenolate for scleroderma has been added to a Medicare-approved compendium.

FDA Approves Nintedanib for SSc-ILD, But Temper Your Expectations
The U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) approved nintedanib for systemic sclerosis associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) on Sept. 6 after a randomized, controlled trial (SENSCIS) demonstrated significant benefit against placebo.1 At a cost of $96,000 per year, treatment reduced the adjusted annual rate of change in forced vital capacity (FVC) from –93.3 mL in…
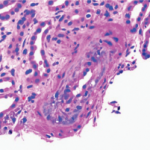
Case Report: A Patient Develops Scleroderma Renal Crisis
Scleroderma renal crisis (SRC) is a life-threatening complication of systemic sclerosis. SRC occurs in 2–15% of patients with diffuse sclerosis and usually within the first five years from the time of diagnosis. Risk factors for SRC include, but are not limited to, early diagnosis, corticosteroid or cyclosporine use, and the presence of anti-RNA polymerase III…

Can REVEAL Tool Predict Survival in SSc-Related Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension?
A prognostic tool developed to predict survival in patients with various forms of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is fairly accurate in predicting survival outcomes for many patients with PAH related to systemic sclerosis (SSc-PAH), according to a new study. However, the prognostic accuracy is less reliable for SSc-PAH patients with the highest risk of death….
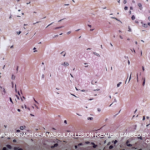
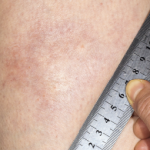
Case Report: Can Salt-&-Pepper Skin Mean Systemic Sclerosis?
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a multi-system connective tissue disease in which skin and internal organ fibrosis are associated with an obliterative micro-vasculopathy and a degree of inflammation.1 Patients often report it takes one to three years from the appearance of the first signs and symptoms before they receive a diagnosis. The signs and symptoms of…
Study Probes New Gene Therapy for Severe, Localized Scleroderma (Morphea)
In September 2018, the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) granted fast-track status to FCX‑013, a gene therapy product developed to treat moderate to severe localized scleroderma (morphea). Previously, the treatment received an orphan drug designation for localized scleroderma, as well as a rare pediatric disease designation. Phase 1 and 2 studies will assess safety…
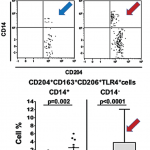
New Studies Identify Possible Markers of Early Systemic Sclerosis
Although the true cause of systemic sclerosis (SSc), or scleroderma, remains unknown, researchers have made progress in detecting the autoimmune disease’s early presence. Beyond the physiological signs of Raynaud’s phenomenon, a capillaroscopy can detect alterations in microcirculation and lab tests can confirm the presence of telltale autoantibodies, such as anti-topoisomerase 1, anti-centromere and anti-RNA polymerase…

Lessons Learned from Two Scleroderma Lung Studies (Plus a Third That’s Recruiting Sites)
Historically, the early approach for treating interstitial lung disease (ILD) due to systemic sclerosis (SSc) involved immunosuppressant therapy, primarily with cytotoxic agents.1 Glucocorticoids in combination with another immunosuppressant agent, such as oral azathioprine or cyclophosphamide, were often used to treat patients with severe, progressive SSc-ILD.2 However, direct evidence to support this therapeutic approach was lacking…
Recent Trials Investigated Targeted Therapies for Systemic Sclerosis
SNOWMASS VILLAGE, COLO.—Data from three recent trials in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) provide information on a number of important issues related to screening and treatment. First presented at the 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting, the phase 2/3 trials assessed the safety and efficacy of targeted agents to treat patients with systemic sclerosis.1-3 In a follow-up presentation at…
Markers for Severe Gastrointestinal Dysmotility in Systemic Sclerosis
A new study from Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, published in the September 2018 issue of Arthritis Care & Research, identifies risk factors and clinical features associated with severe gastrointestinal (GI) dysmotility in patients with systemic sclerosis.1 The findings suggest a distinct pathological process may be at work in this patient group, says lead…
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- …
- 11
- Next Page »