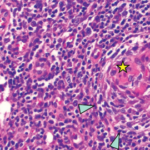
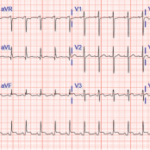
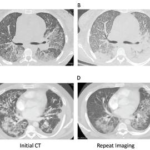
The difference between Castleman disease and Castleman-like disease may be subtle, but it comes with significant ramifications. Case Presentation This case involves a pregnant 19-year-old woman who presents over multiple hospitalizations with concerns for systemic lupus erythematosus and macrophage activation syndrome. At 36 weeks’ gestation, the patient’s weight had dropped from 215 lbs. to 170…