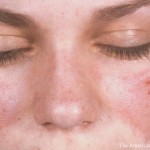
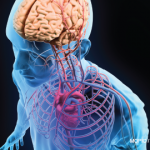
A recent epidemiologic study of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) investigated racial and ethnic differences in the risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Among SLE patients enrolled in Medicaid, the risk for myocardial infarction (MI) was lower in Hispanics and Asians compared with whites, and the risk of stroke was higher in blacks and Hispanics…