NEW YORK (Reuters Health)—An adherent-invasive E. coli pathotype present in the bowel may contribute to the development of Crohn’s disease-associated spondyloarthritis, researchers say. “Clinical symptoms, including extra-intestinal manifestations, in Crohn’s disease offer a portal into the microbial, immune, and genetic mechanisms underlying disease pathogenesis,” Dr. Randy S. Longman from Weill Cornell Medical College in New…

Biomedical Research Key to Advancing Clinical Care for Rheumatic Diseases
WASHINGTON, D.C.—The importance of biomedical research to advancing clinical care with the ultimate goal of improving patients’ lives was on display during an ACR Discovery 2016 plenary session at the 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting. The session offered new ways to think about and treat select rheumatologic diseases, including research showing for the first time the…
Benefits of Secukinumab in Ankylosing Spondylitis May Persist at 2 Years
NEW YORK (Reuters Health)—Secukinumab appears to improve clinical and radiographic outcomes of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) through two years of therapy, according to new results from the MEASURE 1 study. Secukinumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody against interleukin-17A, which is implicated in various pathophysiological features of spondyloarthritis. In a report online Dec. 13 in the…
Fecal Metabolomics Implicate Tryptophan Pathway in Pediatric Spondyloarthritis
Using metabolomic profiling of fecal samples of children with enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA), researchers found that children with ERA may have lower levels of tryptophan metabolites. This finding may be attributable to differences in the gut microbiota that contribute to their pro-inflammatory phenotype…
Rheumatology Drug Updates: Abaloparatide Promising for Osteoporosis, Plus Secukinumab for Ankylosing Spondylitis
Abaloparatide for Osteoporosis Abaloparatide is completing Phase III clinical trials for the potential treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis in women who are at an increased risk of fracture.1 Abaloparatide is a synthetic peptide that engages the parathyroid hormone receptor and has favorable bone building activity. Abaloparatide has completed Phase 3 development for use as a daily…

Abaloparatide Promising for Osteoporosis; NICE Draft Guidelines Include Secukinumab for Ankylosing Spondylitis
In a clinical trial, subcutaneous abaloparatide has proved effective in treating postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Also in the U.K., draft guidelines for treating ankylosing spondylitis will recommend the use of secukinumab…
Sexual Dimorphism Found in Immunologic Profiles of Patients with Ankylosing Spondylosis
A study that found distinct sexual dimorphism in the immunologic profiles of patients with ankylosing spondylosis (AS) suggests that sex is an important variable to address in future research and may eventually lead to more effective sex-specific therapy for patients with the disease. The research, published in the March 2016 issue of Arthritis & Rheumatology,…
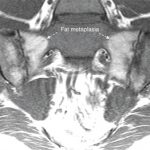
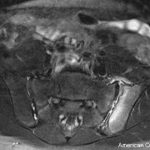
How Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technology Can Aid Spondyloarthritis Diagnosis
SAN FRANCISCO—“We haven’t made a lot of progress in ensuring the early diagnosis of spondyloarthritis,” said Walter Maksymowych, MD, FRCP, professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of Alberta and chief medical officer at CaRE (Canadian Research and Education) Arthritis, both in Edmonton. Speaking at the California Rheumatology Alliance 2016 Medical…
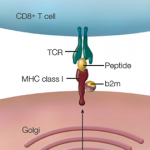
How HLA-B27 Research Landmarks, Advances Relate to Ankylosing Spondylitis Pathogenesis
The mechanistic link between human leukocyte antigen B27 (HLA-B27) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is one of the great enigmas in rheumatology. The introduction of biological therapies that target tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or the interleukin (IL) 23/IL-17A axis has had a major impact on the quality of life for many patients with AS, and one…
Conformational Flexibility in HLA-B27 Provides Clues to Development of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Understanding how human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I molecule B27 promotes spondyloarthritis has intrigued researchers for four decades. Although the association between the single gene variant HLA-B27—specifically some of its subtypes—with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is particularly strong, how HLA-B27 directly influences disease development has not yet been clearly explained, although hypotheses continue to be generated….
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- …
- 19
- Next Page »