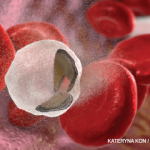
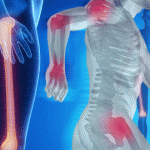
Anemia is common in patients with systemic rheumatic disease, yet it may not get the attention it deserves. Anemia can result from chronic inflammation, treatment side effects or other disease factors, or it may signal an unrelated condition. Although diagnosis and treatment of anemia are sometimes challenging, clinicians must do their utmost to rigorously investigate…