A new study adds to the evidence that metabolic factors play an important role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In this large, prospective cohort study, Liu et al. found that increased physical activity among women was associated with a reduced risk of RA…
Search results for: seropositive
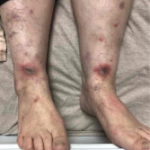
Case Report: RA Patient Suffers Methotrexate-Induced Cutaneous Lesions
Methotrexate (MTX) remains the predominant medication used by rheumatologists to treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Doses of 7.5–25 mg per week with daily folic acid are generally prescribed. Despite its common use, MTX must be prescribed cautiously given the potential adverse effects when taken incorrectly or without folic acid supplementation. Cases of MTX-induced cutaneous ulceration have…
Asthma, Allergic Disease, Passive Smoke Exposure & the Risk of RA
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most common autoimmune diseases. One hypothesis is that inflammation in the respiratory tract results in autoantibody formation that later leads to disease. Kronzer et al. set out to narrow the knowledge gaps related to the oral-respiratory factors that may mediate RA pathogenesis.
Metrics in Rheumatology: Focus on Harold E. (Hal) Paulus, MD
We have just learned that Dr. Hal Paulus passed away on April 5, 2019. We are reposting this story today in his memory and will share additional information as we learn it.
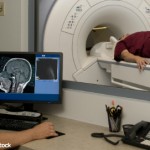
MRI-Guided Therapy Offers No Improvement Over Conventional Treat to Target for RA
New research does not support the use of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-guided strategy for treating RA patients. The study found that among RA patients in remission, an MRI-guided treat-to-target strategy compared with a conventional treat-to-target strategy did not result in improved disease activity remission rates or reduced radiographic progression…

State-of-the-Art Approaches to Rheumatic Disease Diagnosis, Management & Treatment
CHICAGO—Held during the 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting, the ACR Review Course covered a wide range of topics for rheumatologists—from advances in pain and rheumatic disease management to the intersection of rheumatology and neurology. Session speakers shared insights, as well as state-of-the-art approaches to diagnosis, management and treatment. Inflammatory Myopathies Julie J. Paik, MD, MHS, assistant…

The History & Future of Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies (ACPAs)
Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) are now viewed as critical diagnostic and prognostic markers for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Research into the pathophysiology of these autoantibodies has proven to be a ripe area of investigation, opening up many promising avenues for better understanding the etiology and pathogenesis of RA. Ultimately, work utilizing these autoantibodies may also allow…

Recent Research Probes Smoking & the Risk for Autoimmune Disease
It’s no secret to any health professional, including rheumatologists, that smoking cigarettes or using other tobacco-based products is unhealthy. Yet how does smoking specifically affect rheumatic diseases, and what are some of the newest findings in this area? What role do e-cigarettes have in the smoking risk landscape? Those are the sorts of questions asked…

IgG from Patients with Autoimmune Disease Activates Neutrophils
A recent study examined the effects of immunoglobulin G (IgG) on isolated neutrophils of patients with autoimmune disease. Researchers found different autoimmune diseases have distinct patterns of IgG-mediated integrin activation and neutrophil function, which may explain disease-specific differences in vascular damage and dysfunction…
Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk Lower Among Smokers Who Quit
(Reuters Health)—Adults who quit smoking decades ago may have a lower risk of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) than people who gave up cigarettes more recently, a U.S. study suggests. Smoking has long been linked to an increased risk of RA, and quitting can reduce this risk. But the new study offers fresh evidence that years of…
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- …
- 13
- Next Page »