SNOWMASS VILLAGE, COLO.—The study of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) associated vasculitis (AAV) is ongoing, and research results should help improve treatment for this patient population. Key trials and therapeutic options were discussed at the 2020 ACR Winter Symposium during the session, Update on the Treatment of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis, by Peter A. Merkel, MD, MPH, chief of…
Study Probes Whether Belimumab Can Lower Vasculitis Relapse Rate
In an international clinical trial, adding the drug belimumab to standard maintenance therapy for patients in remission with vasculitis did not lower the relapse rate. The double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluated the safety and efficacy of belimumab as adjunctive therapy to maintain remission in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) associated vasculitis (AAV). Results of the multi-center, industry-sponsored…

Thinking Big, Thinking Small
I would like to tell you a story. Two, actually. I am just returning from the 19th International Vasculitis and ANCA Workshop, which is always a fascinating meeting. In its inception, it was a workshop, in the true sense of the word. Now, we discuss anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) testing as casually as we discuss…
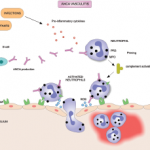
Research Shows Genetic Links in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis
CHICAGO—Ken Smith, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at the University of Cambridge, England, gave an update on anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) at the 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting. Although vasculitis tends to be defined first by vessel size, the clinical differentiation between the forms is not reliable, explained Dr. Smith. For example, granulomatosis with…
AAV Remission Study: Does Rituximab or Azathioprine Work Best?
Researchers sought to identify predictors of patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) associated vasculitis (AAV) who took rituximab for maintenance had a better sustained remission rate through 60 months than those taking azathioprine, according to the latest results from the maintenance of remission using rituximab in systemic ANCA-associated vasculitis (MAINRITSAN) trial, a prospective, randomized trial…
Rituximab Maintenance Study: Is Fixed-Schedule or Tailored Dosing Best?
Rheumatologists prescribe rituximab for induction and maintenance treatment for anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody (ANCA) associated vasculitides (AAV). Maintenance treatment typically employs fixed-schedule dosing, but in the recent maintenance of remission using rituximab in systemic ANCA-associated vasculitis II (MAINRITSAN2) trial, researchers from the French Vasculitis Study Group examined whether individually tailored maintenance dosing might work better. “The…

ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Pathogenesis & Treatment Updates
SAN DIEGO—At the 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting this past November, three researchers discussed the latest ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) research, including studies on AAV pathogenesis, therapies and remission maintenance. In the Philip Hench, MD, Memorial Lecture, J. Charles Jennette, MD, chair in pathology and laboratory medicine at the University of Carolina at Chapel Hill in Chapel…
Changes in BMI Associated with Improvements in Disease Activity & Glucocorticoid Treatment
A recent study examined the relationship between increased BMI and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis treatment with glucocorticoids. The results: Weight gain was independently associated with reductions in disease activity, increased glucocorticoid exposure and randomization to rituximab. The most significant increases in BMI occurred during the first six months of treatment, and newly diagnosed patients were more likely to experience an increase in BMI…
Malignancy Risk in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Is Lower with Rituximab
NEW YORK (Reuters Health)—Compared with cyclophosphamide, rituximab treatment poses less malignancy risk in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV), European researchers report. Dr. Emma E. van Daalen of Leiden University Medical Center in the Netherlands tells Reuters Health, “Previous studies reported an increased malignancy risk in patients with AAV, which has been associated…
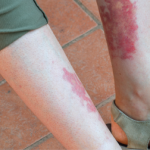
Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage Secondary to Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Vasculitis: Predictors of Respiratory Failure and Clinical Outcomes
A variety of immune and nonimmune pathophysiologic mechanisms causing the disruption of alveolar capillaries with bleeding into the alveolar spaces can lead to diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH). Immune-mediated mechanisms can cause DAH with or without the presence of capillaritis. The antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis (AAV) syndromes—granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA)—are the…