The FDA has approved bimekizumab-bkzx for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis, non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.


The FDA has approved bimekizumab-bkzx for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis, non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
Walter P. Maksymowych, MB ChB, FACP, FRCP(C) |
The axial phenotype of psoriatic arthritis (axPsA) is an excellent example of a major controversy in rheumatology that has become the focus of attention because of the emergence of new therapies with different mechanisms of action for alleviating joint inflammation. It was first described in 1961 but, until recently, it has largely remained under the…
Philip Helliwell, DM, PhD, FRCP |
When Moll and Wright first described the spondyloarthritides in the early 1970s, the archetype of the group was ankylosing spondylitis (AS).1 The shared clinical features of the spondyloarthritides were sacroiliitis; asymmetric large joint peripheral arthritis; psoriasis or psoriaform skin lesions, including keratoderma blennorrhagica; uveitis; and bowel inflammation. Moll and Wright described five clinical subgroups of…

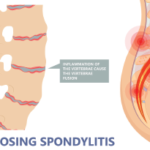
At the 17th Annual Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of the Rheumatic Diseases meeting at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, Atul Deodhar, MD, discussed ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis & clarified common misconceptions about these conditions.

Mary Choy, PharmD, BCGP, FASHP |
Over the past few years, biosimilars and other new drugs have been introduced to treat rheumatic illnesses. Some of the conditions we treat have numerous drug options; others have few or only off-label options. This series, Rheumatology Drugs at a Glance, provides streamlined information on the administration of biologic, biosimilar and other medications used to…
In February A&R, Penso et al. reported on the results of their study, which explored whether patients with psoriasis, PsA and AS have a higher risk of developing IBD when treated with an IL-17 inhibitor compared with apremilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, or etanercept, a TNF inhibitor.
ACR CONVERGENCE 2020—In recent years, a pathophysiological role for the interleukin (IL) 17/IL-23 axis in the development of psoriasis, enthesitis and inflammatory arthritis has been investigated in both rodent and human models. Clinical trials have demonstrated differential benefits for skin disease and joint disease in patients with psoriatic arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) and ankylosing spondylitis…

In January, upadacitinib was approved for use in Europe as a 15 mg, once-daily dose to treat patients with psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.

Three experts discuss the ins and outs of using magnetic resonance imaging to diagnose axial spondyloarthritis, particularly in individuals who lack clear clinical symptoms indicative of disease.

In August, Abbvie submitted a new drug application for upadacitinib to treat ankylosing spondylitis. And in September, the FDA approved an oral solution of tramadol hydrochloride for pain.