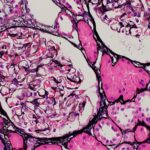
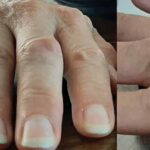
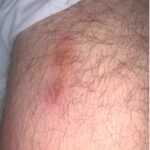
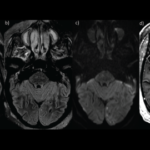
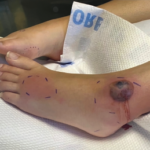
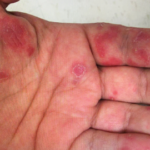
The following report outlines a case of newly diagnosed adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) complicated by macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) in a previously healthy and active 32-year-old man who had emigrated from Africa to the U.S. Case A man with no prior medical history presented with acute-onset polyarthritis, fevers and fatigue that began one month previously….