A recent study from the U.K. calculated the incidence of comorbidity associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), specifically looking for cardiovascular disease, stroke, end-stage renal failure, cancer, osteoporosis and infection. Even after adjusting for age, sex and other variables, investigators found that people with SLE have an increased global burden of comorbidity compared with the general population. Additionally, the study found that men with SLE had higher rates of cardiovascular disease, stroke and cancer, while women with SLE had higher rates of infection and osteoporosis. Overall, younger people with SLE had the greatest relative risk compared with controls…

Bacterial Curli Amyloid: Researchers Examine the Role of Bacterial Infection in Lupus Pathology
New research has found that the amyloid protein curli triggers immune activation and autoantibody production in lupus-prone and wild-type mice. Stefania Gallucci, MD, says these results provide insight into the mechanisms of bacterial infection that may result in lupus…

Innate Immune Response Enters Center Stage for Inflammatory Eye Disease
Researchers suspect the C-type lectin receptor (CLR) mincle may play a role in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. A new study linked CLR mincle to Card9-signaling events and IL-1, resulting in inflammation…

From the Expert: Don’t Forget to Vaccinate Immuncompromised Patients
Preventing infection in immunocompromised patients is challenging, especially with the increased use of biologic treatments, which have been known to reactivate latent infections, such as the herpes zoster virus. Nicolas Issa, MD, discusses recent vaccination research and prevention techniques to help this patient group avoid infection…
Scientists Find How ‘Superbugs’ Build Their Defenses
LONDON (Reuters)—Scientists in Britain have found how drug-resistant bacteria build and maintain a defensive wall—a discovery that paves the way for the development of new drugs to break through the barrier and kill the often deadly “superbugs.” In recent decades, bacteria resistant to multiple drugs, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or Clostridium difficile, have…

2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting: Stroke Risk Elevated after Herpes Zoster Infection Among Patients with Autoimmune Disease
SAN FRANCISCO—The risk of stroke after herpes zoster (HZ) infection is elevated in the period immediately after infection in patients with autoimmune diseases, according to a study presented at the 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting.1 The findings were presented in a scientific session, called Discover 2015, that highlighted new research. In another study from the session,…
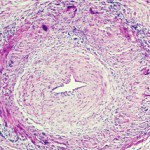
Research in Temporal Arteritis Suggests Link with Infection, Autoimmune Disease
Temporal arteritis was first described by Sir Jonathan Hutchinson in 1890 in an elderly retired gentleman’s servant who developed red, painful streaks on his temples and was found to have bilaterally swollen temporal arteries with feeble pulses.1 Sir Hutchinson disputed the suggestion that the red streaks were caused by the man’s hat and, instead, called…
FDA Warns Makers of Superbug-Prone Scopes over Testing Violations
(Reuters)—Manufacturers of duodenoscopes linked to recent superbug outbreaks at U.S. hospitals skirted a host of testing, manufacturing and reporting requirements, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration said in warning letters to the companies released on Monday. The letters, sent on Aug. 12, cite Olympus Corp Pentax Medical and Fujifilm Holdings Corp with multiple violations found…
Infection & Hospitalization in SLE
From 1996–2011, the rates of hospitalization due to serious infectious diseases in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) increased substantially, according to new research. In a retrospective data-driven study, researchers plotted and compared hospitalization and in-hospital mortality rates of SLE and non-SLE populations, determining the trends for the five most common infections…

Lungs Are Particularly Vulnerable in Patients with Systemic Rheumatic Disease
In an observational study, physicians found that systemic rheumatic disease exacerbation and treatment-related infections were often related to the lungs…