No one-size-fits-all approach exists for the care and treatment of patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) and SSc with pulmonary involvement. Here, experts discuss some best clinical practices for these patients.


No one-size-fits-all approach exists for the care and treatment of patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) and SSc with pulmonary involvement. Here, experts discuss some best clinical practices for these patients.

Melissa Griffith, MD, discussed the diagnosis and treatment of interstitial lung disease (ILD) in patients with rheumatic diseases, including connective tissue disease and more.

ACR Convergence 2021—The past year has been an exciting time for researchers and clinicians focused on the topic of connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease (CTD-ILD), with advances in our understanding of these disorders and newly approved medications for their treatment. At the ACR Convergence 2021 annual Review Course, Kristin Highland, MD, MSCR, director of…
Joshua Solomon, MD, & Paul F. Dellaripa, MD |
Introduction The understanding and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has evolved dramatically in the past 20 years. As gains have been made in treating joint disease in RA, our understanding of the impact of extra-articular manifestations of RA, such as cardiac and lung disease—specifically interstitial lung disease (ILD)—has gradually increased. While rheumatologists increasingly appreciate the…

Treatment with tocilizimab preserved lung function in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) and interstitial lung disease (ILD) regardless of a patient’s level of lung involvement, according to a recent study.
Anusha Vuppala, MD, & Sarwat Umer, MD |
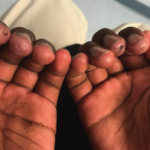
Juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) is a childhood form of inflammatory myopathy affecting children younger than 18 years. The diagnosis of JDM is based on characteristic clinical features of proximal muscle weakness, skin rash, elevated muscle enzymes, magnetic resonance imaging and muscle biopsy.1 Autoantibodies seen in patients with inflammatory myopathy are not only associated with particular phenotypes…
Anusha Vuppala, MD, & Sarwat Umer, MD |
Clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis (CADM), a rare subset of dermatomyositis (DM), is an autoimmune disease characterized by cutaneous findings of typical DM without evidence of myositis. Childhood presentation of CADM is rare, and not many studies describe the epidemiology of juvenile CADM.1,2 Although lung disease is rare among patients with juvenile DM, a few reports have…

Subcutaneous tocilizumab is the first biologic agent approved by the FDA treat patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease.

ACR Convergence panelists discussed how to monitor SSc-ILD patients for ILD severity & the brightening prospects for therapy.
Rajandeep Paik, MD, FACR |
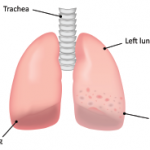
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a heterogeneous group of lung parenchymal disorders that share several clinical, radiologic and histopathologic features, and are therefore grouped together.1 ILD can occur in association with most rheumatic connective tissue diseases (CTDs), but patients with systemic sclerosis, polymyositis, dermatomyositis and rheumatoid arthritis have the highest risk of developing ILD.2 A…