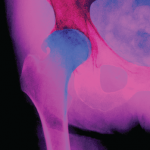
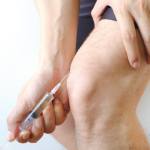
Sir William Osler, the father of modern medicine, said “the desire to take medicine is perhaps the greatest feature that separates man from animal.” Determination of the benefit of a medication can be challenging and includes a number of factors, such as pharmacologic activities on the disease pathophysiology, pharmacokinetic properties and patient characteristics.1,2 An additional,…