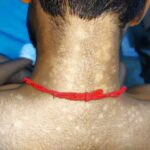
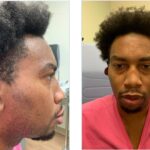
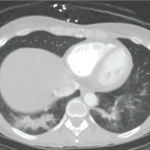
VEXAS is a recently identified rare genetic disorder associated with somatic mutations in the UBA1 gene. Given the variability in disease presentation & the limited number of studies to date, an international multidisciplinary panel of VEXAS experts was convened to provide guidance to healthcare providers on the condition’s management. We spoke to experts on the panel about the resulting guidance document.