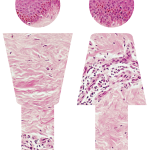
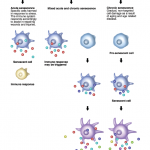
Medications for serious or life-threatening conditions may receive accelerated approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) by showing an effect on surrogate measures that are reasonably likely to predict a treatment’s clinical benefit. Post-approval confirmatory drug trials are then required to determine whether or not these effects translate into clinical improvements. In recent…